Complete CBSE-Ready Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes
(Avoid Common Mistakes)
The chapter Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes explains how industries convert raw materials into finished goods, increasing value and strengthening the economy. Manufacturing forms the backbone of development by supporting agriculture, creating jobs, boosting exports and providing essential products to society.
1. Meaning of Manufacturing
Manufacturing refers to the process of converting raw materials into finished goods using machines, labour and technology. This transformation adds economic value and usefulness.
Cotton → Cloth: Raw cotton fibres are processed, spun and woven to create garments and fabrics useful for daily life.
Iron ore → Steel: Iron ore is melted and purified to create strong steel used for construction, vehicles and machinery.
Timber → Furniture: Wood is cut, shaped and polished into furniture that adds comfort and utility in homes and offices.
Manufacturing is important in Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes because it adds value, improves living standards and forms the base of industrial development.

2. Importance of Manufacturing Industries
Industries play a central role in modern economic systems. Their contribution extends beyond making products.
Reduces unemployment: Factories require labour, technicians and skilled workers, creating widespread job opportunities.
Improves living standards: Manufactured goods like clothing, electronics, tools and transport improve quality of life.
Raises national income: Industrial output increases GDP and strengthens financial stability.
Boosts exports: Manufactured items such as textiles, steel and chemicals enhance foreign exchange earnings.
Modernises agriculture: Industries supply fertilizers, machinery, pesticides and irrigation equipment to improve farm productivity.
Reduces dependence on farming: A strong industrial base diversifies the economy and reduces pressure on agriculture.
Strengthens economic independence: Nations with strong industries rely less on imported goods.
Develops infrastructure: Industries push growth in roads, power supply, communication and transport services.
Countries with powerful industrial sectors are generally more developed due to higher productivity and employment.
3. Contribution of Industry to the National Economy
The Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes highlight India’s slow but consistent industrial growth.
Manufacturing contributes around 17–18% to India’s GDP.
Growth remains slow due to outdated equipment, weak infrastructure and low investment.
The National Manufacturing Policy aims to increase this share to 25% and create 100 million industrial jobs.
Industrial expansion is essential for transforming India from an agricultural economy into a modern industrial nation.
4. Agro-Based Industries
These industries use agricultural raw materials like cotton, jute and sugarcane. They support farmers, rural employment and export growth.
4.1 Textile Industry
The textile industry is India’s largest and oldest industry. It employs millions, contributes to GDP and earns major foreign exchange.
A. Cotton Textile Industry
Raw material – cotton: Soft natural fibre used for spinning yarn and weaving cloth.
Major centres: Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Surat, Coimbatore, Ludhiana, Kanpur — all with cotton-growing regions and labour availability.
Features:
Labour-intensive: Requires large workforce for spinning and weaving tasks.
Decentralised: Many small units produce yarn and cloth across India.
Mixed production: Uses both handlooms, powerlooms and mill-based machinery.
Problems in Cotton Industry
Old machinery: Reduces speed and quality of production.
Power shortages: Frequent electricity cuts slow down factory output.
Competition from synthetics: Nylon, polyester and artificial fibres reduce demand for cotton cloth.
B. Jute Industry
Raw material – jute: Long natural fibre grown mainly in alluvial soil.
Major centres: Hooghly belt in West Bengal — most suitable for jute processing.
India is the largest jute producer globally.
Products: Gunny bags, ropes, carpets, sacks and floor coverings.
Challenges:
Cheap synthetic packaging reduces demand.
Bangladesh offers lower production cost, affecting India’s exports.
C. Sugar Industry
Raw material – sugarcane: Juicy crop used to make sugar, jaggery and ethanol.
Major centres: Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu.
Sugar mills are seasonal because sugarcane supply depends heavily on temperature and rainfall.
TABLE 1 – COMPARISON OF AGRO-BASED INDUSTRIES
| Feature | Cotton Textile | Jute | Sugar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Cotton fibre | Jute fibre | Sugarcane |
| Nature | Labour-intensive | Export-oriented | Seasonal |
| Major States | Maharashtra, Gujarat | West Bengal | UP, Maharashtra |
| Challenges | Old machinery | Synthetic substitutes | Climate-dependent |
5. Mineral-Based Industries
These industries use minerals and ores and are vital for heavy engineering.
5.1 Iron and Steel Industry
Steel is the backbone of industrial development as it supports transportation, construction and machinery sectors.
Major Steel Centres
Jamshedpur, Bhilai, Rourkela, Durgapur, Bokaro, Visakhapatnam.
Conditions Needed for Steel Plants
Raw materials: Iron ore, coal, limestone essential for steel making.
Transport: Railways and roads needed for moving bulky raw materials.
Water supply: Large quantities required for cooling and washing.
Cheap labour: Workers needed for furnace operations and rolling mills.
Reliable power: Electricity required for blast furnaces and machinery.
Problems Faced
High cost of production
Outdated technology
Uncertain power supply
Low productivity of labour
5.2 Aluminium Industry
Raw material – bauxite: Rock containing alumina which is refined to aluminium.
Major states: Odisha, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra.
Properties: Light, corrosion-resistant, strong metal.
Uses: Aircraft, cables, utensils, packaging foils, vehicles.
Aluminium production requires huge electricity, making power availability crucial.
5.3 Cement Industry
Raw materials: Limestone, silica, gypsum.
Major centres: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu.
Cement is crucial for construction of dams, roads and buildings.
6. Chemical Industries
The chemical industry is diverse and supplies essential inputs.
6.1 Heavy Chemicals
Produce acids, alkalis and fertilizers.
Examples: Sulphuric acid, nitric acid, ammonia — used in factories, detergents and fertilizer units.
6.2 Fertilizer Industry
Major centres: Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Punjab.
Produces nitrogenous, phosphatic and mixed fertilizers used to increase crop yield.
Supports agricultural growth by improving soil nutrients.
6.3 Pharmaceutical Industry
Produces vaccines, tablets, syrups and life-saving medicines.
Major centres: Hyderabad, Mumbai, Bangalore.
India is one of the largest exporters of generic medicines.
TABLE 2 – COMPARISON OF MINERAL-BASED INDUSTRIES
| Industry | Raw Material | Key States | Key Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Iron ore, coal | Jharkhand, Odisha | Construction, transport |
| Aluminium | Bauxite | Odisha, TN | Aircraft, cables |
| Cement | Limestone | Rajasthan, MP | Buildings, roads |
7. Light and Small-Scale Industries
These industries require limited capital, small workforce and simple tools.
Examples: Toys, jewellery, garments, furniture, handicrafts.
They generate rural employment, support artisans and help preserve traditional skills.

8. Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
8.1 Air Pollution
Caused by:
Factory smoke containing SO₂, CO₂ and dust particles
Burning coal in power plants
Chemical fumes from steel and fertilizer factories
Effects: Respiratory problems, acid rain, global warming.
8.2 Water Pollution
Caused by:
Dumping of untreated factory waste
Toxic chemicals from tanneries
Oil spills and radioactive discharge
Effects: Death of aquatic life, unsafe drinking water, waterborne diseases.
8.3 Thermal Pollution
Factories release hot water into rivers, reducing oxygen levels and harming fish.
8.4 Noise Pollution
Generated by machinery, construction, generators.
Effects: Hearing issues, stress, irritation, reduced concentration.
9. Measures to Control Industrial Pollution
Treat industrial waste before releasing.
Shift to cleaner fuels like CNG and solar.
Install scrubbers and filters in chimneys.
Recycle solid waste and reuse materials.
Strict laws and monitoring by government.
Keep industries away from densely populated areas.
These measures support sustainability in Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes.
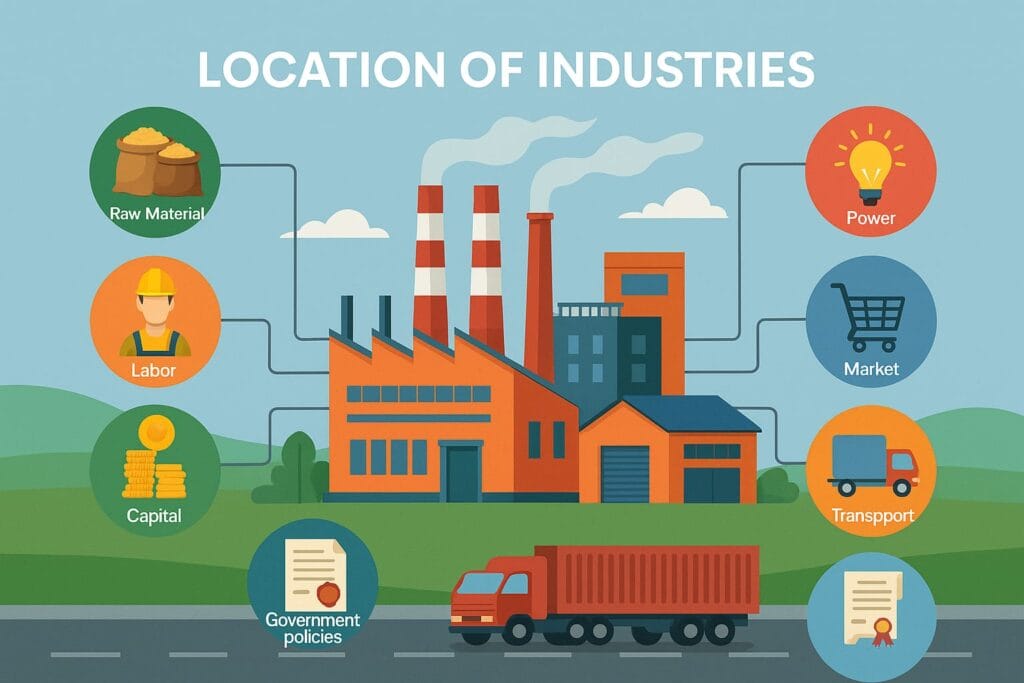
10. Industrial Location Factors
Industries choose their location based on:
Raw materials: Must be nearby to reduce transport cost.
Power: Electricity required for machines.
Transport: Roads/railways for movement.
Water: Needed for cooling and cleaning.
Labour: Cheap and skilled workforce.
Market: Availability of buyers.
Government policy: Incentives and tax benefits.
Climate: Comfortable conditions reduce factory stress.
Industries cluster in areas where these factors combine favourably.
11. Industrial Regions of India
Major industrial belts include:
Mumbai–Pune: Automobiles, engineering, textiles, chemicals.
Ahmedabad–Vadodara: Textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals.
Bangalore–Tamil Nadu: IT, electronics, textiles.
Chotanagpur Plateau: Iron and steel, mining, engineering.
Delhi–Meerut: Electronics, automobiles, engineering.
12. Information Technology and Electronic Industry
The fastest-growing modern sector.
Major IT hubs: Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Gurgaon, Noida.
IT products: Software, chips, computers, servers.
India is a global leader in software and outsourcing services.
13. Industrial Sickness
Industries become “sick” due to:
Outdated machinery
Poor management
Continuous financial losses
Low market demand
Government helps through modernization, financial restructuring and skill training.
14. Role of Government in Industrial Development
Establishing public sector units
Providing subsidies and tax benefits
Creating Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
Encouraging foreign investment
Improving transport and power supply
Launching schemes like Make in India
These steps support industrial growth and employment.
15. Important Terms
Manufacturing: Converting raw materials to finished goods.
Agro-based: Uses products from agriculture.
Mineral-based: Uses ores and minerals.
Pollution: Environmental damage due to harmful substances.
Industrial region: Area with many industries.
PPP: Public-Private Partnership for development.
16. Summary
Manufacturing converts raw materials into finished products, increasing value.
India has agro-based, mineral-based, chemical and IT industries.
Industrial location depends on raw materials, labour, power and market.
Pollution from industries includes air, water, noise and thermal pollution.
Sustainable industrial growth requires strict pollution control and modern technology.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes emphasise the industry’s importance for economic development.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes
FAQs
1: Why is manufacturing important for India’s economic development?
Manufacturing is essential because it transforms raw materials into valuable products, creating employment and improving national income. In Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, manufacturing is highlighted as the backbone of development since it strengthens agriculture, supports exports, and creates large-scale jobs. Industries also develop transport, power and communication infrastructure, which boosts overall growth.
Key Points:
Creates direct and indirect jobs
Helps agriculture through tools and fertilizers
Raises GDP
Improves living standards
2: What are agro-based industries and why are they important?
Agro-based industries use agricultural products like cotton, jute and sugarcane as raw materials. These industries are important because they support farmers, generate rural employment and reduce poverty. The cotton, jute and sugar industries discussed in Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes represent key sectors that help India’s economy diversify beyond agriculture by providing stable non-farm jobs.
Key Points:
Use farm-based raw materials
Provide rural employment
Reduce pressure on agriculture
Support export earnings
3: Why is the iron and steel industry called the backbone of modern industry?
The iron and steel industry is called the backbone because it supplies steel to almost all sectors—construction, machinery, transport, engineering and defence. Without steel, bridges, buildings, railways and factories cannot be built. In Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, this industry is central to industrial development because it supports heavy industries and modern infrastructure.
Key Points:
Provides basic raw material for industries
Required for transport networks
Needed for machinery manufacturing
Supports industrial growth
4: Why are textile industries significant in India?
Textile industries are important because they are India’s oldest and largest industries, providing huge employment. Cotton and jute sectors support both rural and urban workers. As highlighted in Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, textiles also bring foreign exchange through exports and support millions of small-scale units.
Key Points:
India’s largest employer
Supports small-scale industries
Major export contributor
Uses local raw materials
5: What causes industrial pollution and how does it affect the environment?
Industrial pollution occurs due to untreated waste, chimney smoke, chemical discharge, hot water release and excessive noise. In Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, pollution is shown to cause air pollution, water contamination, loss of aquatic life, soil damage and health issues for workers.
Key Points:
Smoke causes respiratory diseases
Effluents pollute rivers
Hot water reduces oxygen levels
Noise causes stress and hearing issues
6: What factors determine the location of industries in India?
Industrial location depends on raw materials, water, electricity, labour, transport, market demand and government policies. Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes explains that industries prefer regions with cheap labour, accessible raw materials and good connectivity. These factors reduce cost and increase profit.
Key Points:
Raw materials reduce transport cost
Power supports machines
Labour ensures smooth operation
Policies encourage investment
7: Why are some industries in India becoming “sick”?
Industries become sick due to outdated machinery, low demand, financial losses and poor management. According to Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, when industries cannot modernise or compete with new technologies, productivity declines. Government support through loans and modernization schemes is required to revive such industries.
Key Points:
Old technology reduces output
Poor management leads to losses
Competition affects sales
Government plans help revival
MCQs
Q1. Which activity best represents manufacturing in the context of industrial development?
A. Growing sugarcane
B. Converting cotton into cloth
C. Selling agricultural goods
D. Mining iron ore
Answer: B
Q2. Which sector benefits the MOST from manufacturing industries by receiving machinery and fertilizers?
A. Education
B. Agriculture
C. Tourism
D. Healthcare
Answer: B
Q3. Which policy aims to increase manufacturing share to 25% and generate millions of jobs?
A. National Mineral Policy
B. National Manufacturing Policy
C. Industrial Disputes Act
D. Start-up India Mission
Answer: B
Q4. Which raw material is primarily used in cotton textile industries?
A. Jute fibre
B. Cotton fibre
C. Polyester
D. Wool
Answer: B
Q5. Which state is known for the Hooghly jute belt?
A. Gujarat
B. West Bengal
C. Punjab
D. Odisha
Answer: B
Q6. Why is sugar industry considered a seasonal industry?
A. Demand varies seasonally
B. Sugarcane supply depends on climate
C. Machines work only in winter
D. Labour migrates often
Answer: B
Q7. Which city is India’s oldest steel manufacturing centre?
A. Bhilai
B. Jamshedpur
C. Bokaro
D. Rourkela
Answer: B
Q8. What is the most essential raw material for aluminium production?
A. Limestone
B. Bauxite
C. Iron ore
D. Copper ore
Answer: B
Q9. Which industry requires the largest supply of electricity to operate the smelting process?
A. Textile industry
B. Sugar industry
C. Aluminium industry
D. Toy manufacturing
Answer: C
Q10. Which raw material is MOST important for cement industries?
A. Gypsum
B. Limestone
C. Coal
D. Mica
Answer: B
Q11. Which chemical is a major product of heavy chemical industries?
A. Baking soda
B. Sulphuric acid
C. Perfume
D. Vitamin tablets
Answer: B
Q12. Which centre is famous for India’s pharmaceutical industry?
A. Hyderabad
B. Coimbatore
C. Kanpur
D. Jaipur
Answer: A
Q13. Which industry produces nitrogenous and phosphatic fertilizers?
A. Cement industry
B. Fertilizer industry
C. Jute industry
D. IT industry
Answer: B
Q14. Which industry primarily supports India’s IT sector?
A. Construction
B. Electrical machinery
C. Electronics and software
D. Food processing
Answer: C
Q15. Which factor affects industrial location the MOST?
A. Trees
B. Availability of raw materials
C. Sports facilities
D. Festivals
Answer: B
Q16. Which region is known as India’s IT hub?
A. Mumbai
B. Hyderabad
C. Bangalore
D. Jaipur
Answer: C
Q17. Which industry is mainly located in Chotanagpur plateau due to minerals?
A. Jute
B. Steel
C. Sugar
D. Pharmaceuticals
Answer: B
Q18. Which is a major cause of air pollution from industries?
A. Rainwater
B. Factory smoke
C. Clean energy
D. Hand tools
Answer: B
Q19. Water pollution occurs mainly because industries release _______.
A. Treated water
B. Kitchen waste
C. Toxic chemicals and effluents
D. Sand
Answer: C
Q20. Thermal pollution is caused when industries release what into rivers?
A. Cold oil
B. Hot water
C. Plastic waste
D. Garbage
Answer: B
Q21. Which type of pollution can lead to hearing loss in factory workers?
A. Water pollution
B. Noise pollution
C. Thermal pollution
D. Soil pollution
Answer: B
Q22. Which measure can reduce pollution in factories?
A. Dumping untreated waste
B. Installing filters in chimneys
C. Using more coal
D. Increasing smoke levels
Answer: B
Q23. What helps industries reduce cost by minimizing transportation charges?
A. Distant market
B. Remote workforce
C. Nearby raw materials
D. Hot climate
Answer: C
Q24. Which belt is known for automobiles and textile manufacturing?
A. Delhi–Meerut
B. Mumbai–Pune
C. Jaipur–Ajmer
D. Patna–Gaya
Answer: B
Q25. The IT and electronics industry mainly produces _______.
A. Furniture
B. Handicrafts
C. Software and chips
D. Sugar
Answer: C
Q26. Which industry often becomes sick due to old machinery and poor management?
A. Steel industry
B. IT industry
C. Textile industry
D. Cement industry
Answer: C
Q27. Government sets up SEZs mainly to _______.
A. Increase pollution
B. Reduce production
C. Encourage industrial growth
D. Decrease employment
Answer: C
Q28. Which industry uses both handlooms and powerlooms?
A. Cement
B. Jute
C. Cotton textile
D. Pharmaceutical
Answer: C
Q29. Which pollution control method involves recycling factory waste?
A. Burning waste
B. Dumping waste
C. Waste reuse and recycling
D. Burying waste
Answer: C
Q30. Industries located near big markets enjoy which main advantage?
A. Faster sales
B. High transport cost
C. Weak labour supply
D. Poor demand
Answer: A
Daily Update: Quizzes, Flashcards, Tests, Worksheets etc are shared .
5-Marker Questions
Q1: Explain the importance of manufacturing industries in India.
Manufacturing industries are vital for India because they convert raw materials into valuable finished goods, leading to economic development. They create large-scale employment, raise national income, support agriculture through machinery and fertilizers, and boost exports. As explained in Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, industries help reduce dependence on agriculture by providing alternative jobs, improving living standards, and strengthening economic independence. Industrial expansion also leads to better infrastructure such as roads, electricity, communication and transport networks, further accelerating growth.
Q2: Describe the major industrial regions of India and explain why industries cluster in these areas.
India’s major industrial regions include Mumbai–Pune, Ahmedabad–Vadodara, Bangalore–Tamil Nadu, Chotanagpur plateau and Delhi–Meerut. These regions attract industries because they offer raw materials, water, labour, transport, electricity and large markets. According to Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, industries cluster in favourable regions to reduce costs, increase efficiency and access customers quickly. Good roads, ports, skilled labour and government incentives make these areas ideal for industrial growth.
Q3: What are the major types of industrial pollution? Explain effects of each.
Industries cause air, water, noise and thermal pollution. Air pollution results from factory smoke and chemicals, leading to respiratory diseases. Water pollution occurs when untreated waste, oil and chemicals enter rivers, harming aquatic life. Noise pollution from machines causes stress and hearing issues. Thermal pollution happens when factories release hot water into rivers, reducing oxygen levels. In Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Notes, these pollutants are shown to damage ecosystems and human health, requiring strict control measures.
Supportive Study Material Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Science Quiz
- Class 10 Science tests
- Class 10 Science Worksheets
- Class 10 Science PYQs
- Class 10 Science NCERT Solution