Complete CBSE-Ready Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes
(Avoid Common Mistakes)
The chapter Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes explains why transport, communication and trade are essential for a country’s economic growth. These systems connect people, move goods, support industries, promote tourism and strengthen national unity. They are called “lifelines” because no sector can operate efficiently without them.
1. Importance of Transport and Communication
Transport and communication are the backbone of modern economic activities because they link producers, consumers, markets and industries.
Enable movement of goods and raw materials: Industries require continuous supply of raw materials and transportation helps them move efficiently.
Connect remote regions: Transport networks ensure that distant villages, mountains, deserts and islands remain linked to the national economy.
Support trade and markets: Goods can be sold across states and countries only if transport networks are strong.
Promote tourism and services: Travel becomes easier, boosting hotels, airlines, tourism, vehicles and local businesses.
Strengthen national unity: Easy movement of people increases cultural understanding and reduces regional imbalance.
Enhance communication: Phones, internet, postal services and media allow information to travel instantly.
2. Modes of Transport in India
India has a diverse transport system suited for different needs.
The major modes include:
Roadways – suitable for short and medium distances
Railways – ideal for long distances and heavy goods
Pipelines – best for oil, gas and liquid movement
Waterways – cheapest for bulky goods
Airways – fastest for passengers and emergencies
Each mode plays a unique role in the Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes and contributes to economic connectivity.
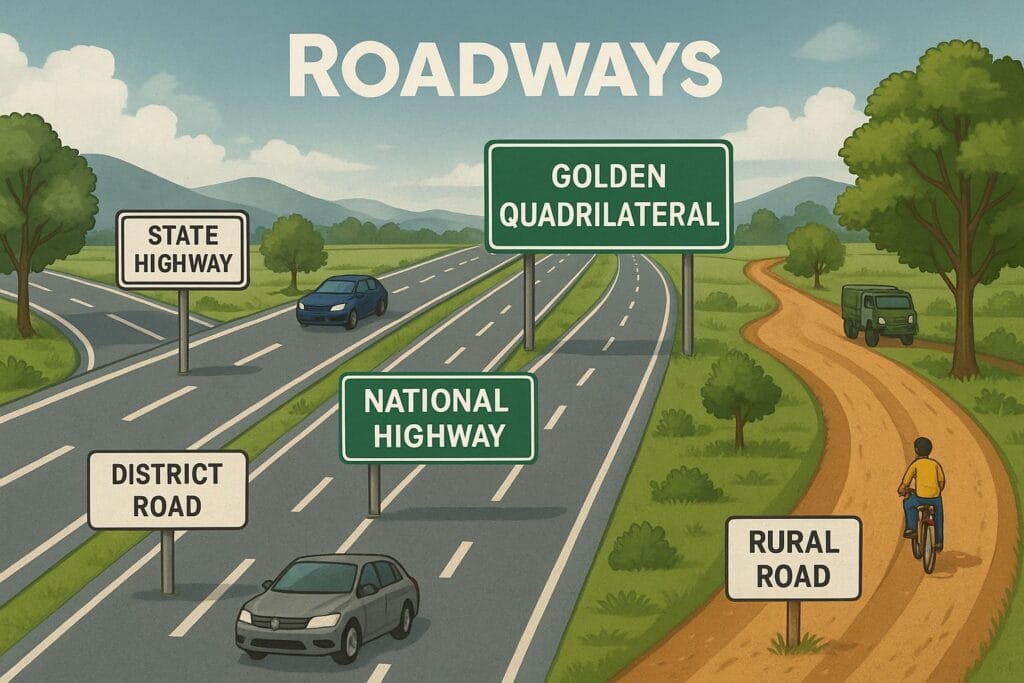
3. Roadways
Roadways carry 85% passengers and 65% freight, making them the most widely used transport mode.
Advantages of Roadways
Door-to-door service: Roads directly connect homes, markets, farms and industries without breaks.
Low construction cost: Roads require less investment compared to railways or airports.
Flexible routes: Vehicles can change paths based on demand or conditions.
Connect remote areas: Hilly areas, deserts, forests and villages depend mainly on roads.
Ideal for perishable goods: Vegetables, milk and fruits reach markets quickly through road transport.
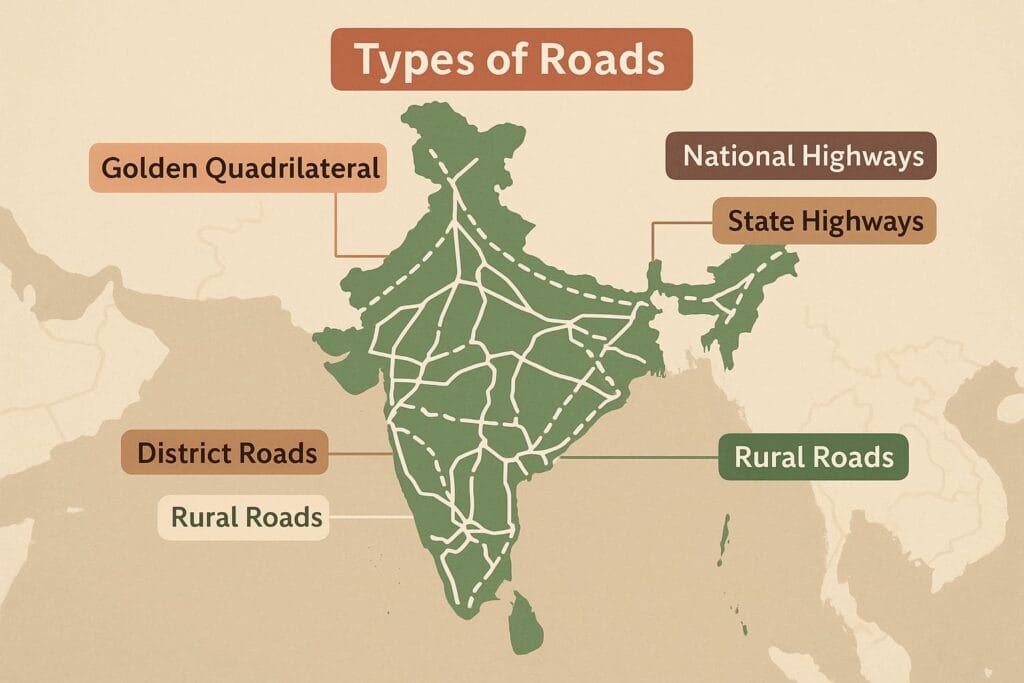
3.1 Types of Roads in India
A. Golden Quadrilateral (GQ)
Connects Delhi–Mumbai–Chennai–Kolkata
Reduces travel time and boosts trade between major cities
Enhances industrial and economic growth across the four corners of India
B. National Highways
Designed and maintained by NHAI
Important examples:
NH-44: Srinagar to Kanyakumari (longest in India)
NH-27: Silchar to Porbandar
Connect major states, ports, industries and tourist regions
C. State Highways
Connect state capitals with district headquarters
Managed by state governments
D. District Roads
Connect district towns with local markets and villages
E. Rural Roads
Built under PMGSY
Provide village connectivity for farmers and rural workers
F. Border Roads
Built by BRO in tough terrains like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh
Help defense movement and strategic connectivity
3.2 Problems of Roadways
Traffic congestion in big cities
Poor maintenance leads to potholes
Increasing accidents due to overcrowding
Pollution from vehicle emissions
Overloading of trucks damages roads
Unequal development across states affects connectivity
🟩 TABLE 1 – COMPARISON OF ROAD TYPES
| Road Type | Managed By | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Highways | NHAI | Connect major cities | NH-44 |
| State Highways | State Govt. | Connect capitals | SH networks |
| Rural Roads | PMGSY | Connect villages | Village roads |
| Border Roads | BRO | Connect border regions | Ladakh roads |
4. Railways
Railways are one of India’s strongest lifelines and essential in Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes due to their massive carrying capacity.
Importance of Railways
Carry heavy and bulky goods like coal, cement and iron
Provide low-cost long-distance travel
Connect industrial areas with ports and markets
Support agriculture by carrying food grains and fertilizers
Provide large-scale employment
Promote national integration
India has the fourth-largest railway network in the world.

4.1 Types of Railway Gauges
Broad Gauge (1.67 m): Used for most major routes; fastest and safest
Metre Gauge (1 m): Used earlier; now being converted to broad gauge
Narrow Gauge (0.762 m): Used in hilly areas; being phased out
Gauge conversion promotes uniformity and improves speed.
4.2 Problems of Railways
Overcrowding in trains
Old tracks causing delays and accidents
Vandalism and theft in certain regions
High maintenance costs
Difficult terrains in North-East and Himalayan regions
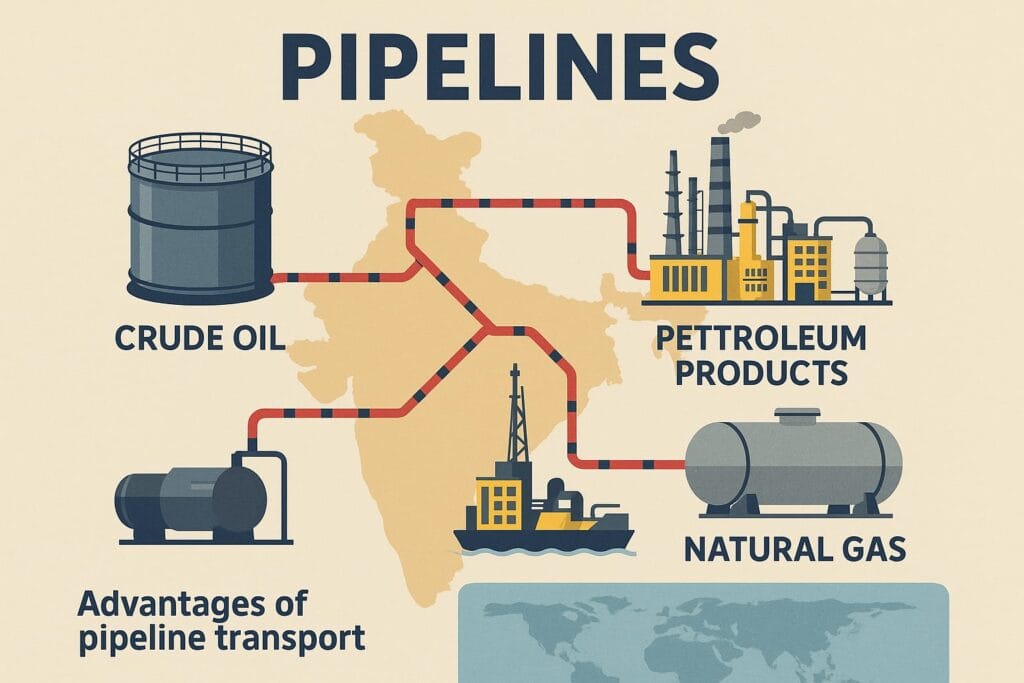
5. Pipelines
Pipelines transport petroleum, natural gas and slurry over long distances.
Advantages
Low operating cost after installation
No fuel requirement and eco-friendly
Safe for transporting inflammable liquids
Reduces rail and road traffic congestion
Useful for remote and difficult terrains
Major Pipeline Routes
Naharkatia → Barauni → Haldia
Hajira → Vijaypur → Jagdishpur (HVJ) gas pipeline
Salaya → Mathura → Jalandhar
Pipelines reduce pollution and ensure efficient movement of resources.
6. Waterways
Waterways are the cheapest and fuel-efficient mode for transporting heavy cargo.
Advantages
Requires minimal fuel
Causes very little pollution
Ideal for long-distance transport of bulky goods
Suitable for international trade via ports
6.1 Inland Waterways
ndia has five major National Waterways:
NW-1: Ganga (Allahabad–Haldia)
NW-2: Brahmaputra (Sadiya–Dhubri)
NW-3: Kerala backwaters
NW-4: Godavari–Krishna rivers
NW-5: Odisha rivers
These rivers support trade, fishing and tourism.
6.2 Sea Routes and Major Ports
India has a coastline of 7,516 km with multiple major ports.
Major Ports and Their Importance
Mumbai: Largest and busiest
JNPT: Biggest container-handling port
Kandla: Specializes in petroleum and fertilizers
Visakhapatnam: Iron ore export hub
Chennai & Kolkata: Historic ports with mixed cargo
Cochin: Natural harbour; handles spices and fishing
Marmagao: Leading iron ore export port
Ports connect India with global markets and enable foreign trade.
🟩 TABLE 2 – MAJOR PORTS AND THEIR SPECIALIZATION
| Port | Location | Specialty |
|---|---|---|
| Mumbai | Maharashtra | Largest port |
| JNPT | Maharashtra | Containers |
| Visakhapatnam | Andhra Pradesh | Iron ore exports |
| Kandla | Gujarat | Petroleum & fertilizers |
| Cochin | Kerala | Natural harbour |
7. Airways
Air transport is the fastest mode and extremely important for emergency, long-distance and remote-area connectivity.
Advantages of Airways
Fastest travel mode
Essential for disaster relief and medical emergencies
Connects mountains, deserts and islands
Ideal for international travel and tourism
Regions Benefiting the Most
Ladakh
North-East states
Andaman & Nicobar Islands
Lakshadweep
India has domestic carriers and international airlines linking major cities worldwide.
8. Communication
Communication means sharing information quickly and effectively.
8.1 Postal Services
India has the largest postal network
Services include speed post, parcels, money order and e-post
Digital improvements have increased speed and reliability
8.2 Telecommunication
Includes mobile networks, internet and broadband
India is one of the world’s fastest-growing telecom markets
Fibre networks improve rural connectivity
8.3 Mass Communication
Communicates with large audiences
Includes newspapers, TV, radio, films and digital media
Helps in education, advertising, entertainment and government campaigns
9. International Trade
International trade means exchange of goods and services between countries.
Importance
Earns foreign exchange for development
Strengthens global economic relationships
Promotes international cooperation
Distributes Indian products across the world
9.1 Major Export Items
Tea, coffee, spices
Textiles and garments
Engineering goods
Chemicals and pharmaceuticals
Gems and jewellery
Petroleum products
9.2 Major Import Items
Crude oil
Gold and silver
Machinery
Electronics
Fertilizers
Chemicals
India often imports more than it exports → trade deficit.
9.3 Balance of Trade
Positive: Exports > Imports
Negative: Imports > Exports
10. Tourism
Tourism is a major service industry supporting millions of jobs.
Importance of Tourism
Earns large foreign exchange
Creates employment in hotels, travel, transport and handicrafts
Promotes cultural understanding and unity
Supports regional development
Major Attractions
Taj Mahal, Hampi
Hill stations like Shimla, Ooty
Beaches of Goa and Kerala
National parks
Religious destinations like Varanasi and Amritsar
11. Problems in Transport and Communication
Road congestion and pollution
Overcrowded trains
Poor rural connectivity
High cost of air travel
Slow development of waterways
Digital divide in rural regions
Shortage of modern infrastructure
12. Important Terms
Golden Quadrilateral: Network connecting four major metros
National Highway: Major roads maintained by NHAI
Port: Hub for international trade via ships
Mass Communication: Media used to reach large audiences
Inland Waterway: Navigable rivers and canals
International Trade: Exchange of goods between nations
13. Summary
Transport and communication are critical lifelines for India’s economy.
Roadways, railways, waterways, airways and pipelines serve different purposes.
Communication networks like telecom and postal services connect millions.
Ports and airports link India to the world.
International trade and tourism contribute significantly to the economy.
Improving transport and communication ensures balanced national growth.
CBSE Class 10 Geography – Chapter 7
FAQs
1: Why are transport and communication called lifelines of national economy?
Transport and communication are called lifelines because they support every economic activity by ensuring smooth movement of goods, raw materials, people and information. In Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, these systems connect rural areas to markets, help industries function, promote tourism and enable national integration. Without efficient transport and communication, trade slows down, markets collapse and development becomes uneven.
Key Points:
Enable movement
Support trade
Connect remote areas
Boost unity
2: What are the major modes of transport in India?
India has five major modes of transport—roadways, railways, airways, waterways and pipelines. Each serves different purposes depending on distance, terrain and economic activity. In Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, roadways dominate short distances, railways carry heavy goods, pipelines move petroleum, waterways are cheapest for bulk cargo, and airways provide fastest travel.
Key Points:
Roadways: flexible
Railways: heavy loads
Pipelines: liquids
Waterways: cheapest
Airways: fastest
3: What is the importance of waterways in India?
Waterways are important because they are fuel-efficient, eco-friendly and ideal for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances. According to Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, India’s National Waterways support trade, tourism and inland transport. They reduce pressure on roads and railways, lowering congestion and pollution.
Key Points:
Cheapest mode
Good for heavy cargo
Low pollution
Connects ports
4: Why is air transport important in India?
Air transport is crucial because it connects remote, mountainous, desert and island regions that other modes cannot reach. In Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, airways play a major role in disaster relief, rescue operations, and fast long-distance travel. It supports business, tourism and emergency medical services.
Key Points:
Fastest
Essential for remote areas
Supports tourism
Helpful for emergencies
5: What is international trade and why is it important for India?
International trade refers to the exchange of goods and services between countries. It is important for India because it earns foreign exchange, expands markets for Indian goods, and strengthens global relations. In Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, trade supports development by exporting textiles, engineering goods, pharmaceuticals and importing essential items like crude oil.
Key Points:
Earns forex
Supports industry
Strengthens ties
Reduces shortages
6: What are the major ports of India and why are they important?
Major ports such as Mumbai, JNPT, Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Kolkata and Cochin facilitate India’s international trade. According to Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, ports handle petroleum, iron ore, containers, fertilizers and agricultural products. They act as international gateways for export and import.
Key Points:
Handle cargo
Support trade
Connect globally
Strengthen economy
7: What are the main problems faced by India’s transport and communication sector?
India faces issues like road congestion, railway overcrowding, poor rural connectivity, high air travel costs, slow development of waterways and digital divide in villages. In Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, weak infrastructure and uneven development are major challenges affecting smooth transport and communication.
Key Points:
Congestion
Poor rural networks
High air fares
Digital gap
MCQs
Q1. Which sector depends MOST directly on efficient transport systems?
A. Agriculture
B. Entertainment
C. Sports
D. Literature
Answer: A
Q2. Why are transport and communication called lifelines of the economy?
A. They entertain people
B. They help circulate goods and information
C. They reduce population
D. They increase agricultural land
Answer: B
Q3. Which of the following is India’s MOST used transport mode?
A. Airways
B. Roadways
C. Waterways
D. Cable cars
Answer: B
Q4. What connects Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata?
A. Border Roads
B. National Waterways
C. Golden Quadrilateral
D. HVJ Pipeline
Answer: C
Q5. NH-44 connects which two points?
A. Delhi to Chennai
B. Srinagar to Kanyakumari
C. Amritsar to Kolkata
D. Jaipur to Siliguri
Answer: B
Q6. Which roads connect villages and markets?
A. Border roads
B. State highways
C. District roads
D. National highways
Answer: C
Q7. Roadways are more flexible because they:
A. Have fixed routes
B. Allow route changes as per need
C. Require no fuel
D. Are only in cities
Answer: B
Q8. Which gauge is the widest in Indian Railways?
A. Narrow gauge
B. Metre gauge
C. Broad gauge
D. Mini gauge
Answer: C
Q9. Which of the following is a DISADVANTAGE of railways?
A. Carry heavy loads
B. Fast long-distance travel
C. Delays due to old tracks
D. Cost-effective transport
Answer: C
Q10. Pipelines are MOST suitable for transporting:
A. Vegetables
B. Textiles
C. Petroleum and gas
D. Furniture
Answer: C
Q11. Which pipeline connects Hajira, Vijaypur and Jagdishpur?
A. HBJ
B. HVJ
C. NH-27
D. GQ
Answer: B
Q12. Which is India’s cheapest transport mode?
A. Air transport
B. Rail transport
C. Waterways
D. Road transport
Answer: C
Q13. NW-1 lies along which major river?
A. Yamuna
B. Ganga
C. Narmada
D. Cauvery
Answer: B
Q14. Visakhapatnam port mainly exports:
A. Tea
B. Cotton
C. Iron ore
D. Petroleum
Answer: C
Q15. JNPT port is known for handling mostly:
A. Coal
B. Containers
C. Timber
D. Spices
Answer: B
Q16. Which transport mode is MOST crucial during disasters?
A. Roadways
B. Railways
C. Airways
D. Canals
Answer: C
Q17. Which region benefits most from air transport?
A. Plains of Punjab
B. Hilly regions of North-East
C. Coastal Gujarat
D. Desert of UAE
Answer: B
Q18. India’s largest postal network facility is:
A. Radio
B. TV
C. Internet
D. Postal services
Answer: D
Q19. Which is NOT an example of mass communication?
A. TV
B. Radio
C. Letters
D. Newspapers
Answer: C
Q20. International trade refers to exchange of goods between:
A. States
B. Districts
C. Countries
D. Villages
Answer: C
Q21. Which is India’s MAIN export product?
A. Gold
B. Petroleum products
C. Iron ore
D. Fertilizers
Answer: B
Q22. India mostly imports which product in large quantity?
A. Toys
B. Pulses
C. Crude oil
D. Spices
Answer: C
Q23. When imports exceed exports, balance of trade becomes:
A. Equal
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. Balanced
Answer: C
Q24. Tourism helps the economy mainly because it:
A. Increases pollution
B. Creates employment
C. Reduces culture
D. Replaces agriculture
Answer: B
Q25. Which of the following is a major challenge in India’s transport?
A. Too many airports
B. Road congestion
C. Low population
D. Extra railway seats
Answer: B
Q26. Which transport mode BEST connects Andaman & Nicobar Islands?
A. Roadways
B. Railways
C. Airways
D. Pipelines
Answer: C
Q27. The national waterways use which kind of routes?
A. Underground tunnels
B. Canals and navigable rivers
C. Ropeways
D. Highways
Answer: B
Q28. Which service allows fastest communication?
A. Speed post
B. Emails and internet
C. Newspapers
D. Radio
Answer: B
Q29. Which mode is MOST suitable for bulky goods like coal and cement?
A. Planes
B. Trucks
C. Railways
D. Scooters
Answer: C
Q30. Border Roads Organization (BRO) mainly constructs roads in:
A. Plains
B. Coastal regions
C. Desert cities
D. Border and tough terrains
Answer: D
Daily Update: Quizzes, Flashcards, Tests, Worksheets etc are shared .
5-Marker Questions
1: Explain the importance of transport and communication in India’s economic development.
Transport and communication are vital because they link producers, consumers, markets and industries. Efficient transport supports agriculture by carrying raw materials, fertilizers and food grains. Industries rely on roads, railways and pipelines to supply goods nationwide. Communication systems like postal services, internet and telecom ensure fast information flow. As explained in Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, these systems promote national integration, support tourism, enable global trade and reduce regional imbalance. Together, they boost GDP, expand markets and ensure balanced development.
2: Describe the major modes of transport in India and explain their significance.
India has five major transport modes—roadways, railways, pipelines, waterways and airways. Roadways offer flexible and door-to-door movement, while railways handle heavy and long-distance loads. Pipelines transport petroleum efficiently, reducing road congestion. Waterways provide the cheapest method for bulk cargo. Airways ensure fast connectivity, especially in remote regions. As stated in Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, each mode has its own importance, supporting agriculture, trade, tourism and industrial growth. Together, they form a strong national transport network.
3: What are the major exports and imports of India? Explain the importance of international trade.
India’s major exports include textiles, engineering goods, chemicals, gems, jewellery, agricultural products and petroleum items. Imports include crude oil, machinery, gold, silver, fertilizers and electronics. International trade is important because it earns foreign exchange, strengthens global connections, supports Indian industries and helps meet shortages of essential goods. According to Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 Notes, foreign trade expands markets for Indian products and ensures availability of modern goods. It plays a crucial role in economic development and modernization.
Supportive Study Material Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Science Quiz
- Class 10 Science tests
- Class 10 Science Worksheets
- Class 10 Science PYQs
- Class 10 Science NCERT Solution